Diagnostic care will ensure proper diagnosis for congenital or acquired orthopedic or musculoskeletal conditions. Many of these tests, such as an X-ray or MRI, are done in our Cherese Mari Laulhere Imaging Center.
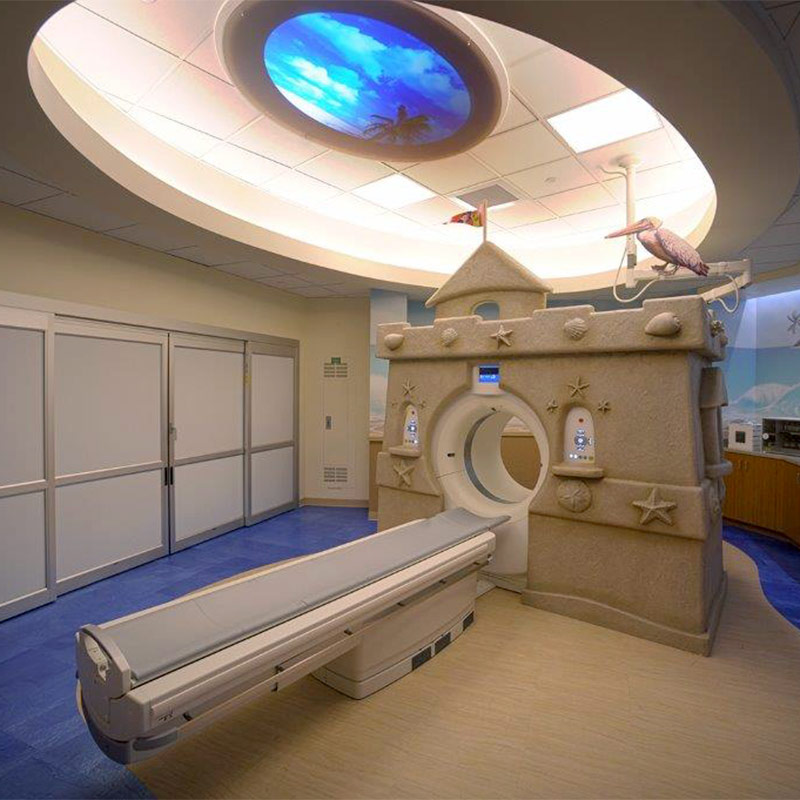
The Imaging Center offers kid-sized equipment to ease anxieties of children needing an imaging test. The pediatric MRI machine is even designed to look like a sand castle. To help prepare children for their imaging scan, there is a miniature MRI built for stuffed animals, so children can see what the test will be like before they are taken back.
Diagnostic Tests
The EOS Imaging System is the first technology capable of providing full-body, 2D and 3D images of pediatric patients in a standing position at a low dose of radiation. EOS is a device that captures bi-planar images with two perpendicular X-ray beams that travel vertically while scanning the patient from head to toe. In less than 20 seconds, the EOS exam produces simultaneous frontal and lateral, low dose images. The two resulting digital images are processed by EOS’ proprietary sterEOS® software to generate a 3D model of the patient’s spine and/or lower limbs. These detailed images with only 20 seconds of radiation were previously unachievable before EOS technology.
The full-body, weight-bearing images provided from a patient standing assists the physicians in diagnosing the patient, as well as developing customized surgical plans. Because of the lower dose of radiation, it is ideal for children who require multiple X-rays during the course of their treatment, such as patients with scoliosis.
A diagnostic test using invisible electromagnetic energy to create images of internal tissues, bones and organs onto film.
A diagnostic test using invisible electromagnetic energy to create images of internal tissues, bones and organs onto film to measure and evaluate the curve. In a full-spine x-ray, the physician or radiologist measures the angle of the spinal curve to determine the correct course of treatment.
A nuclear imaging test is used to rule out any infection or fractures. It also can be used to evaluate any degenerative and/or arthritic changes in the joints and determine the cause of bone pain or inflammation.
A diagnostic imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves and a computer to create images of blood vessels, tissues and organs. Ultrasounds are used to view internal organs as they function and to assess blood flow through various vessels.
A diagnostic procedure that produces detailed images of the organs and body structures. This is used to rule out any associated abnormalities of the spinal cord and nerves.
A CT scan shows detailed images of any part of the body, including the bones, muscles, fat, and organs.
A laboratory analysis is performed on a blood sample that is usually extracted from a vein in the arm using a needle or via a fingerprick.